This web page was produced as an assignment for Gen677 at UW-Madison Spring 2009.
Gene Ontology
AmiGO
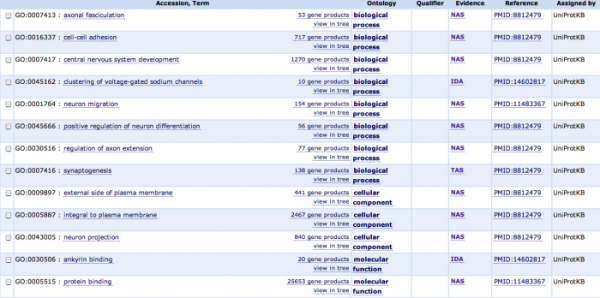
The information below is from the GO Consortium, and is a listing of the GO terms for NrCAM. There are 13 listings, 8 of which are biological process terms that focus on the development of the central nervous system and brain development. Processes such as axonal growth/formation as well as sodium channel development and synaptogenesis are important GO terms as they offer information about why NrCAM is a nice target for autism research. These results were about what I expected before doing my searches as I knew the gene was heavily implicated in brain and central nervous system development. I got an idea about the specificity of the gene's role in brain/CNS development, it appears to play a significant role in the formation of neural networks which depend on axon extension, cell-cell adhesion, and synaptogenesis. The ankyrin and protein binding molecular functions support the possibility that NrCAM is involved in cell-cell adhesion as ankyrin is a plasma membrane protein involved in cell-cell binding. This cell-cell (neuron-neuron) interaction is very important in setting up neuronal networks, and its implications in autism are logical as autistic individuals have defects in several neuronal functions. These functions are all supportive of the predicted localization of NrCAM to the plasma membrane which is also predicted by gene ontology; NrCAM is integral to the plasma membrane and present on the external side of the plasma membrane according to AmiGO.
gp-details.cgi?gp=UniProtKB:Q92823&session_id=6078amigo1242246699.
GOA
Phenotypes
C. elegans WormBase
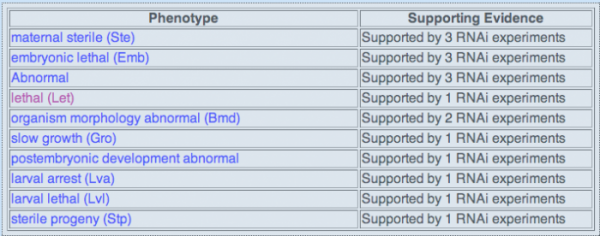
WormBase provides a wide range of entries when doing gene searches. The information includes gene ontology, expression maps in C. elegans, and gene homology information in addition to RNAi experimental data. From the database, I will only provide information related to observed phenotypes in RNAi experiments.
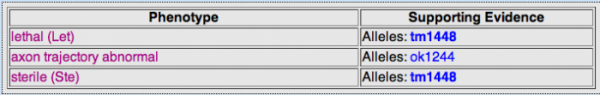
WormBase returned three phenotypes seen in RNAi experiments as seen in Table 1 below. Experimental data can be viewed by clicking on the individual phenotypes in the table which link out to the publications as well as general information about the experiments. The abnormal axon trajectory phenotype is interesting and is concistent with the gene ontology data presented above. This provides support for the research of NrCAM in autism as the development of neuronal networks seems to be abnormal in individuals with autism. Also, the lethal phenotype also speaks to the importance of the LAD-1 gene and protein in C. elegans.
RNAi Database
D. melanogaster RNAi database: Drosophila RNAi Screening Center
Analysis
Brett Maricque
[email protected]
Last updated: 5/13/09
http://www.gen677.weebly.com